Difference between revisions of "Hydra"
Nltwikiadmin (talk | contribs) (Added Initial Description) |
Nltwikiadmin (talk | contribs) m (→32px|left Scripts) |
||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
halt | halt | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | A script consists of both executable and non-executable lines.<br /> | ||
| + | Non-executable lines are either comments that you can use to document or empty lines.<br /> | ||
| + | A comment line always starts with # (pound sign) followed by an optional line of text.<br /> | ||
| + | Empty lines are typically used for formatting purposes to easier read the script.<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Executable lines have a single command with options that perform some kind of action.<br /> | ||
| + | Only one command per line is allowed.<br /> | ||
| + | Every command is terminated by a carriage return.<br /> | ||
=== [[File:Tool_Zone.png|32px|left ]] No-fly zones === | === [[File:Tool_Zone.png|32px|left ]] No-fly zones === | ||
Revision as of 16:01, 10 June 2017
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Components of a mission
- 3 Creating a new mission
- 4 About the Tool Pallet
- 5 Map modification Tools
- 6 Markers
- 7 Rulers
- 8 No-fly Zones
- 9 Routes
- 10 Simulators
- 11 Robot & Simulator Operation
- 12 Robot telemetry
- 13 Scenario Operation
- 14 Mission Planner Settings
- 15 Equipment Settings
- 16 Setting up the wifi network
Introduction
Components of a mission
The map
Markers
Markers are used to indicate points of interest in the arena.
They also indicate special locations such as the base station's GPS antenna and home location for a robot to return to.
Markers are indicated by ![]() in the arena view and selecting a marker will show its name.
in the arena view and selecting a marker will show its name.
A special marker indicated by ![]() shows the location of the home position of a robot.
shows the location of the home position of a robot.
| To add a marker, select the marker icon Click on the arena map to place the new marker. The bottom tip is the exact
location. |
| To move a marker, select the edit marker icon This allows you to select and move the marker to a new location. |
| To indicate the base station's GPS antenna location, use the GPS icon from the
maker tool palette. Only one antenna location is allowed. |
Markers can be renamed in the marker list.
To delete a marker, click on the marker's delete button in the marker list.
Routes
Scripts
One of the more powerful features of planning a mission is using a script to describe a unique motion per robot.
While routes give you basic motion from A to B with a specific speed, script allows you to stop, turn, and vary the speed from waypoint to waypoint based on timing.
Syntax
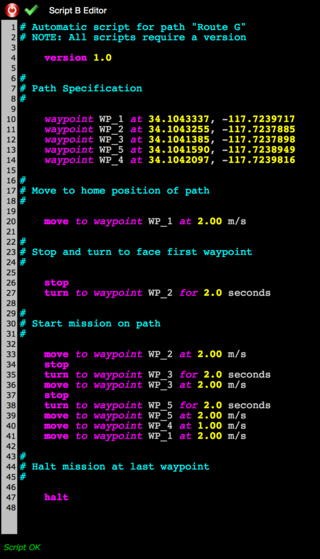
A typical script is structured like this:
# Automatic script for path "Route G"
# NOTE: All scripts require a version
version 1.0
#
# Path Specification
#
waypoint WP_1 at 34.1043337, -117.7239717
waypoint WP_2 at 34.1043255, -117.7237885
waypoint WP_3 at 34.1041385, -117.7237898
waypoint WP_5 at 34.1041590, -117.7238949
waypoint WP_4 at 34.1042097, -117.7239816
#
# Move to home position of path
#
move to waypoint WP_1 at 2.00 m/s
#
# Stop and turn to face first waypoint
#
stop
turn to waypoint WP_2 for 2.0 seconds
#
# Start mission on path
#
move to waypoint WP_2 at 2.00 m/s
stop
turn to waypoint WP_3 for 2.0 seconds
move to waypoint WP_3 at 2.00 m/s
stop
turn to waypoint WP_5 for 2.0 seconds
move to waypoint WP_5 at 2.00 m/s
move to waypoint WP_4 at 1.00 m/s
move to waypoint WP_1 at 2.00 m/s
#
# Halt mission at last waypoint
#
halt
A script consists of both executable and non-executable lines.
Non-executable lines are either comments that you can use to document or empty lines.
A comment line always starts with # (pound sign) followed by an optional line of text.
Empty lines are typically used for formatting purposes to easier read the script.
Executable lines have a single command with options that perform some kind of action.
Only one command per line is allowed.
Every command is terminated by a carriage return.
No-fly zones
Rulers
This feature allows you to measure distances and orientation angle relative to true north.
| Click on the ruler edit icon Click on either end to reposition it, or click on the line connection the two ends to move the whole ruler. |
About Mission files
Creating a new mission
From Lat/Long
Address lookup
From a GPS unit
About the Tool Pallet
Tool tips
Drawing element visibility
Special Tool Functions
Creating a simulator
Creating a script
Map modification Tools
Map parameter editing
Robot shifting
Map shifting
Markers
Purpose
Creating a marker
Editing a marker
Renaming
The Base Station Marker
Rulers
Purpose
Creating a ruler
Editing a ruler
Renaming
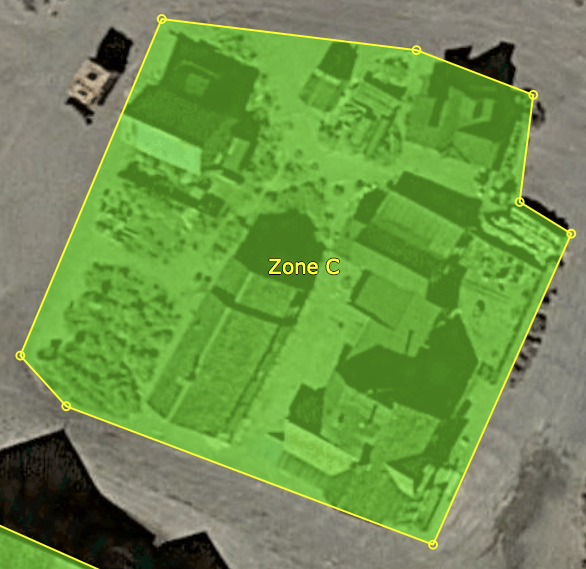
No-fly Zones
Purpose
Creating a no-fly zone
The Arena Boundary Zone
Editing a no-fly zone
Renaming
Routes
Elements of a route
Waypoints
Legs
Creating a route
Route options
Closed Loop
Smooth Path
Visual Aids
Route Length
Confidence
Sharp turn indication
Editing route elements
Inserting waypoints
Translating a route
Duplicating a route
Additional information
Renaming
Deleting
Locking
Fixing
Simulators
Creating a simulator
Robot & Simulator Operation
Device Status Display
Device name
Mission assignment
Heartbeat indicator
Battery indicator
RF Link quality indicator
INS Status
Device Track Display
RF Signal Mode
GPS Mode
Assigning the mission
Operational Controls
Play/Pause
Stop
Playback direction
Repeat/Oscillate
Go to beginning
Go to end
Line Up
Go to Home
Manual
Robot telemetry
Master Alarm
Scenario Operation
Heading text
Joystick-controlled Playback Speed
Mission Planner Settings
Distance Units
Max Track Samples
Track sample spacing
Telemetry samples
Local GPS unit
Equipment Settings
Setting up the wifi network
Connecting via ethernet
- Plug in ethernet cable
- Set PC to manual IP address 192.168.0.51 mask 255.255.255.0
- Open browser to 192.168.0.50
- Go to Dashboard. Click Stop wlan0.
- Click Refresh. Make sure that it says “Interface is down”
- Go to System. Click Restart Robot.
- Launch Mission Planner.
- Perform firmware upgrade.
- Verify that new firmware is running.
- Quit Mission Planner
- Open browser to 192.168.0.50
- Go to Dashboard. Click Start wlan0.
- Disconnect ethernet cable.
- Open browser to robot name e.g. Hydra-170401-1.local
- Go to System. Click Restart Robot.
- Launch Mission Planner.
- Verify connectivity.